Everything You Need To Know About Universal Graphic Driver | Pros, Cons, Tips & More
Outdated graphics drivers can cause visual hiccups, poor performance, and incompatibilities with the newest software in today’s tech environment. Updating your drivers regularly is essential for preserving system stability and maximizing the capabilities of your hardware. With the potential to streamline driver management across various platforms and devices, universal graphic drivers have become a ground-breaking solution. A universal graphic driver provides more interoperability and easier maintenance than conventional manufacturer-specific drivers.
From installation and optimization to resolving frequent problems, this thorough guide covers all you need to know about universal graphic drivers, enabling you to optimize your graphics performance with the least amount of fuss.

What Is a Universal Graphic Driver?
A software program created to work with several graphics processing units (GPUs) from various manufacturers is known as a universal graphic driver. Universal graphic drivers seek to provide a common interface and feature set that is compatible with different GPU architectures, in contrast to conventional proprietary drivers that are tailored to particular hardware models.
It functions similarly to a generic printer driver, enabling your operating system to connect to a range of printer models for simple printing jobs. For display output, the universal graphic driver aims for a comparable degree of wide compatibility. We’ll go into more depth later, but it’s important to realize that this “universality” frequently comes with trade-offs.
Important Features of Universal Graphics Drivers:
1. Support for several vendors: Compatible with GPUs made by NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel.
2. Compatibility with several operating systems: Works with different OSes.
3. Simplified Management: Management is made simpler by managing a single driver package rather than several vendor-specific ones.
4. API Implementation: Standardized access to graphics hardware functions is made possible by consistent API implementation.
5. Less reliance on updates from manufacturers: Reduced dependence on update cycles particular to a vendor.
Types of Universal Graphic Drivers
- Open-source universal drivers (such as Linux’s Mesa)
- Universal drivers embedded into the OS (Windows DCH drivers)
- Cross-platform APIs for graphics (DirectX, Metal, Vulkan)
- The drivers for the emulation layer (DXVK, Wine graphics translation layers)
Why the Shift to Universal Drivers?
The creation of universal graphic driver solutions has been fueled by the increasing difficulty of maintaining numerous driver codebases as well as the requirement for cross-platform compatibility in contemporary applications. All parties involved in the graphics ecosystem can benefit from this strategy:
- For users: Wider compatibility and easier updates
- For developers: A more stable target environment
- For producers: Lower development costs
- Regarding operating systems: Improved stability and integration
How Universal Graphic Drivers Work?
A universal graphic driver functions at a more basic level than manufacturer-specific drivers, which are highly tailored for specific GPU architectures and feature sets. Usually, it implements the fundamental interfaces and display protocols that the operating system supports. This enables it to interact with a variety of graphics devices for essential features like:
- Support for Basic Resolution and Refresh Rate: This allows the display to produce images at common refresh rates and resolutions.
- Colour Depth: Complementing standard colour schemes.
- Basic Graphic Rendering: Enabling the operating system and apps to carry out basic drawing tasks is known as basic graphics rendering.
Nevertheless, universal graphic drivers frequently lack the sophisticated features and optimizations present in vendor-specific drivers to achieve this wide compatibility. This implies that you may lose out on:
- Hardware Acceleration for Advanced Graphics: DirectX, OpenGL, and Vulkan are examples of features that may have little to no hardware acceleration, which can result in subpar performance in graphically demanding applications and games.
- GPU-Specific Features: Likely, proprietary additions such as ray tracing, AMD’s FidelityFX Super Resolution, and NVIDIA’s DLSS won’t be available.
- Power Management Optimizations: Unlike universal graphic drivers, vendor-specific drivers frequently provide power-saving capabilities designed for their hardware.
- Optimal Performance: A universal graphic driver’s generic nature means it isn’t optimized for any particular GPU, which could lead to lower frame rates and less fluid performance, particularly in demanding activities.
Advantages of Using Universal Graphic Drivers
Performance Benefits:
Several performance advantages can be obtained using universal graphic drivers:
1. Resource allocation that is optimized: Improved system resource management for various applications
2. Lower overhead: Reduced processing overhead results from a simplified driver architecture.
3. Uniform feature implementation: a standardized method for accelerating hardware
4. Cross-platform compatibility: Programs run more reliably on several platforms.
Compatibility Benefits:
Improved interoperability is among the most important benefits of a universal graphic driver:
1. Compatible with a variety of GPU brands: NVIDIA, AMD, Intel, and other graphics processors are supported.
2. OS flexibility: Works with Linux, macOS, Windows, and occasionally mobile systems.
3. Support for legacy hardware: Frequently keeps older graphics cards compatible.
4. Future-proofing: By using standardized interfaces, hardware releases can be better anticipated.
Maintenance Benefits:
It is much simpler to manage drivers:
1. One update procedure: Rather than updating several vendor-specific driver packages, update just one.
2. Fewer conflicts: Software conflicts between various driver components are less likely to occur.
3. Streamlined troubleshooting: standardized procedures for reporting and fixing errors.
4. More frequent updates: Compared to certain proprietary systems, these are frequently updated more frequently.
Disadvantages of Using Universal Graphic Drivers
1. Limited enhancements: No optimizations or sophisticated graphics enhancements.
2. Suboptimal Performance: This leads to less fluid visuals and lower frame rates, particularly in demanding applications.
3. Possible Instability: Although they are made to be widely compatible, on some hardware they may not be as reliable as vendor-specific drivers.
4. Lack of Access to Proprietary Technologies: It’s likely that features like FreeSync/G-Sync, ray tracing, and DLSS won’t be available.
5. Limited Support: Because a universal graphic driver isn’t directly supported by the hardware vendor, troubleshooting problems with it can be more difficult.
When Should You (and Shouldn’t) Use a Universal Graphic Driver?
Understanding the benefits and drawbacks aids in deciding when it might be acceptable to use a universal graphic driver:
When it could be helpful:
- Before the installation of particular drivers.
- To rule out driver issues related to a certain vendor, troubleshoot display issues.
- On older hardware when certain drivers are difficult to locate, these jobs include word processing and web browsing, which are not graphically demanding.
- Virtual machines are used to give guest operating systems a display interface.
- When a manufacturer no longer supports a certain driver.
When you should generally avoid it:
- You’ll lose out on important features and noticeably degraded performance.
- There will be significant limitations on tasks like CAD, 3D rendering, and video editing.
- You will be losing out on important features and performance gains.
- The drivers created especially for your graphics card should always come first.
Popular Universal Graphic Driver Solutions
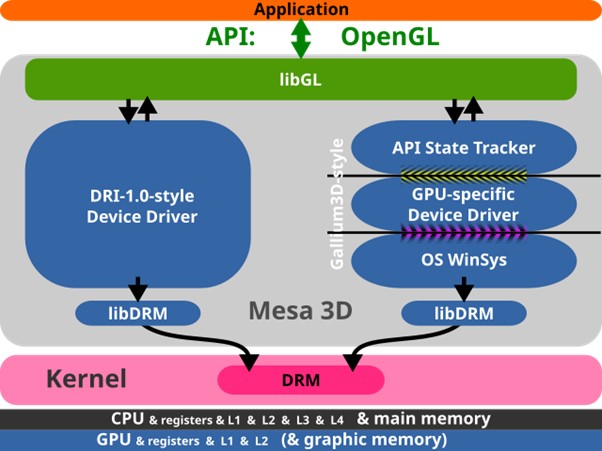
Mesa 3D Visual Aids Collection
One of the most well-known implementations of a universal graphic driver, Mesa is mostly used for Linux and other Unix-like systems:
1. OpenGL, Vulkan, and other graphics APIs implemented in an open-source manner.
2. Utilizes several backend drivers to support AMD, Intel, and NVIDIA technology.
3. Constantly updated and maintained.
4. Gives most Linux versions their graphical power.
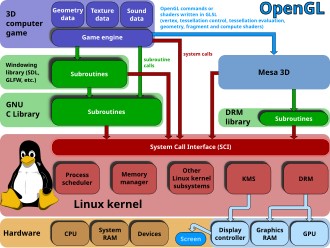
Drivers for Windows DCH
One step toward more ubiquitous driver implementations is Microsoft’s Device Component Hardware (DCH) driver model:
1. A modular design with hardware-specific components and a universal base.
2. Accessible via Windows Update.
3. Accommodates a variety of graphics hardware.
4. Developed for increased security and stability.
Vulkan Drivers and API
Technically speaking, Vulkan is an API rather than a driver, although its methodology makes it possible to develop drivers more broadly:
- Cross-platform and cross-vendor graphics and computation API.
- Developed entirely for driver implementers to produce more all-encompassing solutions.
- Compared to earlier-generation APIs, lower-level access to graphics hardware.
- All of the main GPU suppliers support it.

Getting Ready for Installation
Take these actions before installing a universal graphic driver:
Pre-Installation Preparation
1. Check compatibility: Make sure the universal driver supports your device.
2. Clear out outdated drivers: To get rid of any outdated graphics drivers, use DDU.
3. Get the most recent version: Get the official source of the universal graphic driver.
4. End all programs: Make sure no apps are making excessive use of the GPU.
5. Make a system restore point: As a precaution, make a restore point for Windows users.
Installation Process
Installing a universal graphic driver usually entails the following steps:
1. Start the installer: Open the installer package that has been downloaded.
2. Choose your installation choices: Select between custom and expedited installation.
3. Await device detection: The installer will look for compatible hardware.
4. Finish the installation: To complete the process, adhere to the on-screen directions.
5. Give your system a restart: To make sure all driver components are initialized correctly.
Post-Installation Verification
Make that the universal graphic driver is operating properly after installing it:
1. Verify that the driver: Is correctly identified by checking the device manager.
2. Launch diagnostic tools: Make use of the integrated driver testing tools.
3. Check for API support: Verify that the necessary graphics APIs are supported.
4. Test with apps: To verify performance, run graphics-intensive apps.
5. Monitor Temp: Keep an eye on temps to make sure thermal control is operating correctly.
Writer’s Tip: Optimizing Content About Universal Graphic Drivers
Take into account the following strategies when writing for technical audiences on universal graphic drivers:
1. Strike a balance between accessibility and technical depth: Give readers who might not be as tech-savvy enough precise information without becoming overbearing.
2. Make use of comparison tables: Readers can better grasp the distinctions between proprietary and universal drivers by seeing visual comparisons between them.
3. Provide real-world benchmarks: Actual performance measurements are appreciated by readers.
4. Clear up common misunderstandings: It’s important to clear up frequent misunderstandings that consumers have regarding universal drivers.
5. Offer detailed instructions: The article’s usefulness is increased with thorough installation and troubleshooting instructions that include screenshots.
6. Take into account various user scenarios: The priorities of casual users, professional artists, and gamers differ.
Conclusion:
A major advancement in graphics processing technology, universal graphic drivers provide a more seamless and uniform experience across many hardware platforms. For many users, especially those who value simplicity, cross-platform compatibility, and lower maintenance overhead, the universal method offers appealing benefits, even though old proprietary drivers still have some advantages in particular situations.
Universal graphic driver solutions are expected to advance in sophistication as hardware and software ecosystems continue to change, which might help close the remaining performance and feature gaps with proprietary alternatives. A universal graphic driver is an alluring choice for consumers looking for a mix of compatibility, performance, and usability. It streamlines the computing process while providing strong graphics capabilities.
PEOPLE ALSO ASK:
Q1. What is a universal graphic driver’s primary benefit?
A1. The main benefit is compatibility with various GPU platforms and manufacturers, which makes driver maintenance easier and lowers the possibility of conflicts.
Q2. Are all GPU brands compatible with universal graphic drivers?
A2. Major GPU manufacturers including NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel are supported by the majority of universal graphic drivers; however, support for very new or very old hardware may differ.
Q3. Do OEM drivers outperform universal graphic drivers in terms of stability?
A3: Universal graphic drivers may not be as well-tested and tailored for particular hardware as the manufacturers’ drivers, despite being made for wide compatibility. On some systems, this can result in stability problems.
Q4. How frequently should my universal graphics driver be updated?
A4: Updates should be made whenever new features are required, when issues arise, or for routine maintenance every three to six months, just as with any other driver.
Q5. After utilizing a universal driver, is it possible to revert to a proprietary one?
A5: Yes, but to prevent conflicts, it is advised to fully delete the universal graphic driver before installing a proprietary one.
Q6. Is it safe to use universal graphic drivers?
A6: Universal graphic drivers are just as safe as proprietary ones when they come from reliable sources. Downloads should always come from reliable repositories or official websites.
Q7. Does gaming make use of universal graphic drivers?
A7: Of course! They frequently support sophisticated APIs like Vulkan and DirectX and incorporate improvements for well-known games.
NEXT READ:
- How to Update Graphics Driver on Windows 11/10 [2025 Guide]
- Driver Pack Solution: Complete Review (Unbiased & Updated)
- What is DDU? Full Guide to Use Display Driver Uninstaller
- Best Ways To Handle Windows 11 Driver Updates Issues: Complete Guide
- How To Update Drivers On Windows 11 Automatically & Manually
- Download Epson L3110 Driver for Windows 11/10/7 [Top 3 Ways]
Popular Post
Recent Post
How To Get More Storage On PC Without Deleting Anything [2025]
Running out of space on your PC is frustrating. You might think deleting files is the only way. But that’s not true. There are many ways to get more storage without losing your important data. Learning how to get more storage on PC can save you time and stress. These methods work well and keep […]
How To Speed Up An Old Laptop [Windows 11/10]: Complte Guide
Is your old laptop running slowly? You’re not alone. Many people face this issue as their computers age. Learning how to speed up an old laptop is easier than you think. Over time, older laptops tend to slow down for a variety of reasons. Fortunately, with a few smart tweaks, you can significantly boost their […]
How To Reset Your PC For A Fresh Start In Windows 11/10 [2025]
Is your Windows computer lagging or behaving unpredictably? Are you constantly dealing with system errors, crashes, or sluggish performance? When troubleshooting doesn’t help, performing a full reset might be the most effective way to restore stability. Resetting your PC clears out all installed applications, personal files, and custom settings. It restores the system to its […]
How To Adjust Display Brightness Settings Easily in Windows [2025]
If your screen is overly bright or dim, it can strain your eyes and make tasks uncomfortable. Fortunately, Windows offers simple tools to fine-tune your display brightness. Despite how easy it is, many users aren’t aware of these quick fixes. Windows has many built-in tools to help you. You can change brightness with just a […]
How to Uninstall Problematic Windows Updates Easily [2025]
Learn how to uninstall problematic Windows updates easily. 5 proven methods to fix crashes, boot issues & performance problems. Simple step-by-step guide.
15 Most Essential Windows 11 Privacy And Security Settings [2025]
Learn 15 essential Windows 11 privacy and security settings to protect your data. Master computer privacy settings with simple steps to manage privacy settings effectively.
Rename Your Device For Better Security Windows [Windows 11 & 10]
Learn to rename your device for better security Windows 11 & 10. Simple steps to protect your computer from hackers. Improve privacy and security now.
How To Adjust Display Appearance Settings Easily in Windows 11/10
Learn to adjust display appearance settings easily Windows offers. Simple guide covers brightness, scaling, resolution & multi-monitor setup for better screen experience.
Supercharge Your Productivity: A Solopreneur’s and SMB’s Guide to Mastering Google Workspace with Gemini’
Picture this. It’s Monday morning. You open your laptop. Email notifications flood your screen. Your to-do list has 47 items. Three clients need proposals by Friday. Your spreadsheet crashed yesterday. The presentation for tomorrow’s meeting is half-finished. Sound familiar? Most small business owners live this reality. They jump between apps. They lose files. They spend […]
9 Quick Tips: How To Optimize Computer Performance
Learn how to optimize computer performance with simple steps. Clean hard drives, remove unused programs, and boost speed. No technical skills needed. Start today!